MADISON, Wis. – Republican presidential candidate Scott Walker is hoping to pull his campaign off the mat by taking on unions – a familiar foe for the Wisconsin governor – in a sweeping plan to upend pillars of organized labor nationwide.
Walker’s plan calls for eliminating unions for employees of the federal government, making all workplaces right-to-work unless individual states vote otherwise and scrapping the federal agency that oversees unfair labor practices.
Union leaders are livid. Tony Reardon, president of the National Treasury Employees Union that represents 150,000 federal workers, said Walker is “declaring a war on middle-class workers.” And Democratic presidential contender Hillary Rodham Clinton accused him of bullying union members.
One of Walker’s Republican rivals challenged the plan, too, saying it is the wrong message for the GOP to send to unionized workers. “Instead of treating all union members like they are the enemy,” said former Arkansas Gov. Mike Huckabee, “it’s time we invite them to give some of us in our party a try.”
In an interview with The Associated Press on Monday, Walker said no one should be surprised.
“I think people would be shocked if the governor who took on big government special interests wouldn’t do it at the federal level,” Walker said by telephone as he waited to board a plane to Nevada.
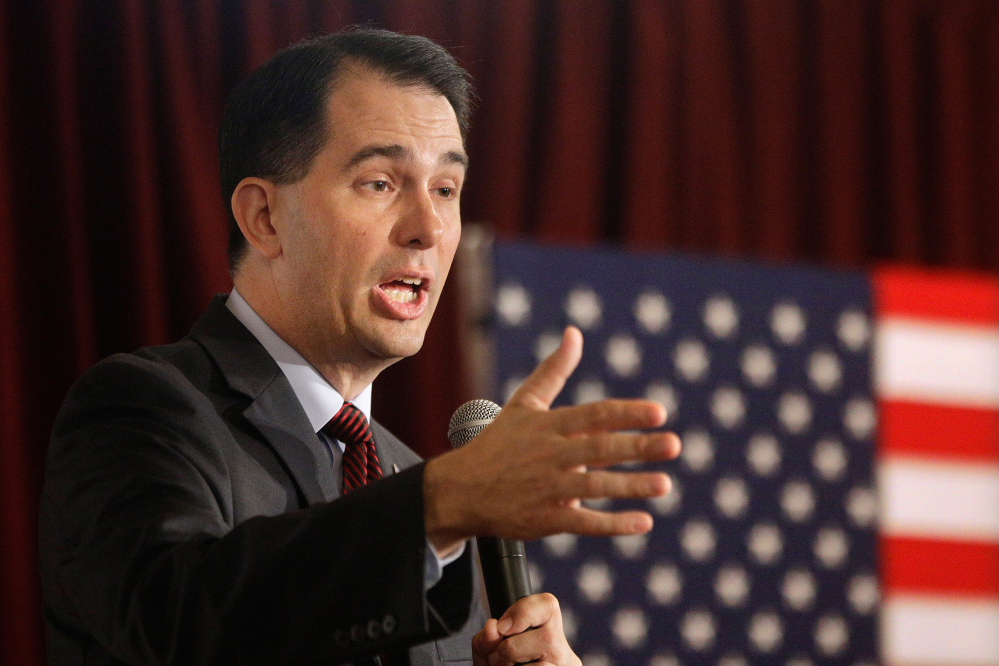
In his speech spelling out his “Power to the People” proposal at a Las Vegas manufacturer, Walker said he didn’t back down against union protesters in Wisconsin and he was ready for the national fight.
“Collective bargaining is not a right, it is an expensive entitlement,” he said, speaking with his sleeves rolled up, in between a pair of oversized construction vehicles and in front of a large American flag.
The move comes as Walker tries to gain traction heading into the second GOP presidential debate, being held Wednesday in California. A weak performance in the first debate and a series of missteps has contributed to his tumble from the polls after his strong start months ago.
“I think it’s a good move,” said Richard Schwarm, a former GOP chairman in the early caucus state of Iowa who is uncommitted in the 2016 race. “It gets a lot of attention on him in the next day or two.”
Walker won nationwide recognition for eviscerating public-sector unions in Wisconsin and becoming the first governor to prevail in a recall election, which followed huge protests against his anti-union steps. Now he’s proposing to go national with an effort to curb union clout.
“It’s reminding people of the reason they liked us in the first place,” Walker said in the interview, brushing aside with laughter a question about whether the move was a sign of desperation.
The reaction from labor groups and Democrats, their traditional political ally, was fierce.
“Scott Walker can now add one-trick pony to his resume, right underneath national disgrace,” said AFL-CIO spokesman Eric Hauser. “His campaign is floundering and so he does what he always does when he can’t think of real solutions. He attacks workers.”
J. David Cox, president of the American Federation of Government Employees, the largest union of federal workers, representing about 750,000 people, said it’s a last-ditch effort by a failing candidate.
“It appears to me that Scott Walker is pretty much desperate in his campaign right now as he’s sinking to the bottom of the polls,” Cox said. “This is desperate action on the part of a very desperate candidate.”
Clinton said on Twitter that unions make families strong.
“Scott Walker’s attacks on unions and workers’ rights aren’t leadership – they’re bullying,” she said.
Her main Democratic rival, Vermont Sen. Bernie Sanders, said Walker’s plan would only make rich people and corporations even wealthier. “If we are going to rebuild the crumbling middle class we need a stronger trade-union movement, not a weaker one,” he said in a statement.
Labor law experts were taken aback by the scope of Walker’s proposal, which seeks to undo decades of law and would gut the landmark National Labor Relations Act – adopted in 1935 and signed into law by President Franklin D. Roosevelt at the height of the Great Depression.
“I’ve never seen anything like this,” said Ann Hodges, a professor at the University of Richmond who has studied labor law for more than 40 years. “This will take the breath away from anyone who’s worked in labor relations for any length of time. … It’s pretty draconian.”
Walker’s plan also calls for prohibiting the automatic withdrawal of union dues to be used for political purposes and forbidding union organizers from accessing employees’ personal information, such as their phone numbers.
While Walker could enact some of the proposals via presidential executive order, the most far-reaching ones would require an act of Congress, a major barrier by any measure.
Walker rose to national prominence in 2011, when just six weeks after taking office as governor, he proposed effectively ending collective bargaining for most public workers in Wisconsin. In the face of protests that often numbered in the tens of thousands, Walker forced the changes through the state Legislature – even after Democratic lawmakers fled the state in an unsuccessful effort to stave off his plans.
Democrats responded by forcing Walker into the 2012 recall, when he notched another victory. He’s since made Wisconsin a right-to-work state, meaning workers can’t be required to pay union dues as a condition of employment.
Send questions/comments to the editors.


Success. Please wait for the page to reload. If the page does not reload within 5 seconds, please refresh the page.
Enter your email and password to access comments.
Hi, to comment on stories you must . This profile is in addition to your subscription and website login.
Already have a commenting profile? .
Invalid username/password.
Please check your email to confirm and complete your registration.
Only subscribers are eligible to post comments. Please subscribe or login first for digital access. Here’s why.
Use the form below to reset your password. When you've submitted your account email, we will send an email with a reset code.