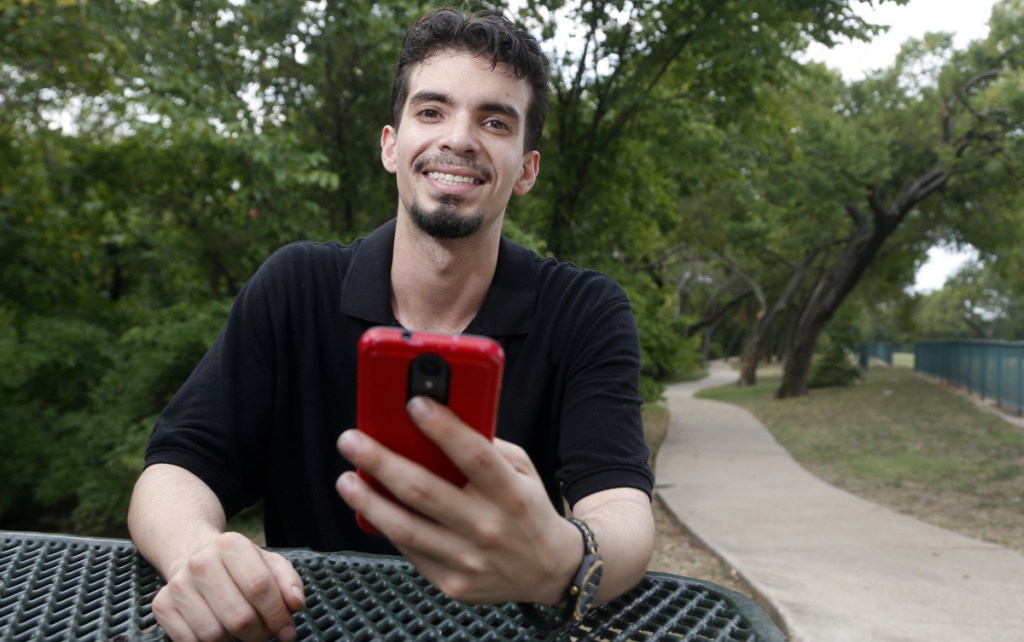
Luis Vazquez and his girlfriend were down to their last $50 after she got sick and had to miss work for a month.
He already paid his rent and bills for the month, but without her income the couple couldn’t cover groceries and other essentials. His next paycheck was more than a week away.
Faced with a similar cash crunch years ago, Vazquez had resorted to a payday loan, a high-interest, short-term loan meant to tide a borrower over until the next paycheck. But the couple and their toddler son were eventually evicted from their apartment because they couldn’t make both their rent and the loan payments.
Vazquez vowed never to take out such a loan again. This time, he had another option. An overnight support manager at Walmart, Vazquez was able to get a $150 advance on his pay using an app that allows the company’s employees to access up to half their earned wages during a pay period.
A growing number of companies are rolling out products and services that allow employees to receive a portion of their pay when they need it. This can help workers, especially those making hourly wages or working irregular schedules, to avoid unpleasant and potentially costly options such as borrowing from loved ones, running up credit card debt, selling possessions or taking out payday or other high-interest loans when bills come due or emergencies arise before the next paycheck.
Could this be the future of payday? Developers of flexible-pay services say adhering to a rigid pay cycle doesn’t make sense.
Josh Reeves, CEO and co-founder of the payroll company Gusto, sees a model in the way parents pay their kids for doing chores.
“If they mow the lawn, they get paid right away,” Reeves said. “We think in the future, everyone will get paid (for their work) when they do it.”
Some experts acknowledge that giving employees early access to their pay can backfire if, for instance, they spend the money unwisely. But the need for flexible pay services is clear. About one-third of U.S. adults were either unable to pay their monthly bills or were one modest financial setback away from financial hardship last year, according to a recent survey by the Federal Reserve.
Vazquez started working at Walmart in November and says he used the app six times since Walmart made it available in December. The app was developed by the technology company Even.
Vazquez pays $6 a month to use the app – there is no transaction fee. By comparison, a payday loan typically carries an annual percentage rate of 300 percent to 500 percent and is due in a lump sum, or balloon payment, on the borrower’s next payday. Vazquez didn’t provide the terms of the payday loan he took out years ago.
“It gives me peace of mind,” he said.
Newer companies such as Uber and Lyft have used immediate payment as their model for years. Now other organizations are catching on to the advantages of a flexible payday.
Jon Schlossberg, CEO of Even, says more than 200,000 of Walmart’s 1.4 million U.S. employees use his company’s app, which also has a cash flow projection feature that deducts upcoming bills from expected pay and shows users an “okay to spend” balance.
Gusto, which provides its payroll services to more than 60,000 businesses nationwide, recently began offering its flexible pay option as an add-on feature at no cost to employers or employees. The company just launched the service in Texas and plans to expand it to additional states later this year.
There’s a tremendous need for such services in the U.S. for several reasons, says Rachel Schneider of the Aspen Institute Financial Security Program and co-author of the book “The Financial Diaries: How American Families Cope in a World of Uncertainty.”
Income and spending needs are volatile and don’t always match up. While some households might be able to make their finances work on paper over the course of a year, they could end up short in any given month, she says.
Some families can build up savings to provide a cushion. But for many workers, the cost of living is outpacing wage growth by such a wide margin that “expecting them to save their way out of volatility is not realistic,” Schneider said.
Cutting checks for every employee used to be time-consuming and costly for companies, which partly explains why many have spread out the pay period. Now the process is largely automated and new technology has enabled more flexibility.
Send questions/comments to the editors.



Success. Please wait for the page to reload. If the page does not reload within 5 seconds, please refresh the page.
Enter your email and password to access comments.
Hi, to comment on stories you must . This profile is in addition to your subscription and website login.
Already have a commenting profile? .
Invalid username/password.
Please check your email to confirm and complete your registration.
Only subscribers are eligible to post comments. Please subscribe or login first for digital access. Here’s why.
Use the form below to reset your password. When you've submitted your account email, we will send an email with a reset code.