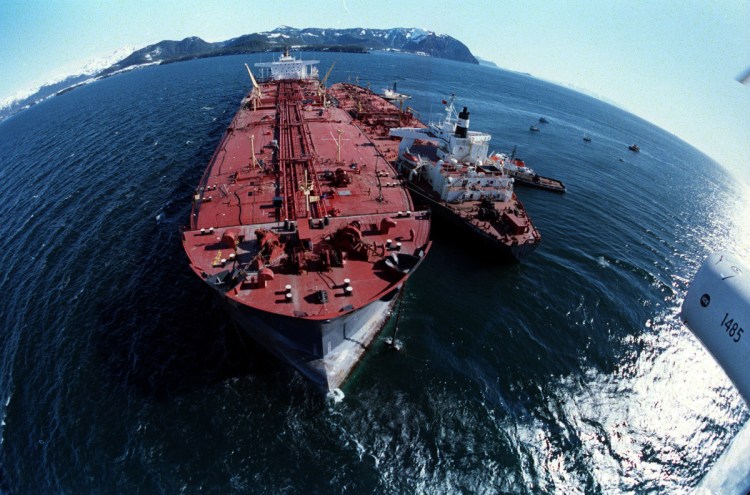
ANCHORAGE, Alaska — It was just after midnight on March 24, 1989, when an Exxon Shipping Co. tanker ran aground outside the town of Valdez, Alaska, spewing millions of gallons of thick, toxic crude oil into the pristine Prince William Sound.

The Exxon Valdez spill took a heavy toll on wildife along 1,300 miles of shoreline. Associated Press/Jack Smith
The world watched the aftermath unfold: scores of herring, sea otters and birds soaked in oil, and hundreds of miles of shoreline polluted. Commercial fishermen in the area saw their careers hit bottom.
This month marks 30 years since the disaster, at the time the largest oil spill in U.S. history. Only the 2010 Deep Water Horizon disaster in the Gulf of Mexico has eclipsed it.
The 986-foot Exxon Valdez tanker was bound for California when it struck Alaska’s Bligh Reef at 12:04 a.m. It spilled 11 million gallons of crude oil, which storms and currents smeared across 1,300 miles of shoreline.
The oil extensively fouled spawning habitat in Prince William Sound for herring and pink salmon, two of its most important commercial fish species.
Fishermen and others affected by the spill dealt with ruined livelihoods, broken marriages and suicides. Exxon compensation checks, minus what fishermen earned on spill work, arrived too late for many.
Most of the affected species have recovered, but the spill led to wide-scale changes in the oil industry. Today, North Slope oil must be transported in double-hull tankers, which must be escorted by two tugs. Radar monitors the vessel’s position as well as that of icebergs.
Send questions/comments to the editors.


Success. Please wait for the page to reload. If the page does not reload within 5 seconds, please refresh the page.
Enter your email and password to access comments.
Hi, to comment on stories you must . This profile is in addition to your subscription and website login.
Already have a commenting profile? .
Invalid username/password.
Please check your email to confirm and complete your registration.
Only subscribers are eligible to post comments. Please subscribe or login first for digital access. Here’s why.
Use the form below to reset your password. When you've submitted your account email, we will send an email with a reset code.